VPS Best Practices
This guide provides UI/UX best practices for implementing VPS (Visual Positioning System) in your application. Since VPS requires camera access and user interaction, providing a clear and intuitive experience is crucial for user adoption and success.
This guide is for the web version of the positioning SDK. Mobile version guide is coming soon.
User Onboarding
Explain What VPS Is
Before requesting camera permissions, help users understand why VPS is needed and what it does. Users are more likely to grant permissions when they understand the value.
Key points to communicate:
- VPS provides accurate indoor positioning
- It uses the camera to recognize the environment
- It uses the sensors to follow the user's movement
- The camera is only used temporarily during scanning
Permission Management
Request Flow
Request permissions in a logical sequence:
- First, explain why - Show a brief explanation screen before requesting permissions
- Request camera permission - Use clear, contextual messaging
- Request sensor permission (iOS) - Explain device orientation needs
- Handle denials gracefully - Provide clear next steps if permissions are denied
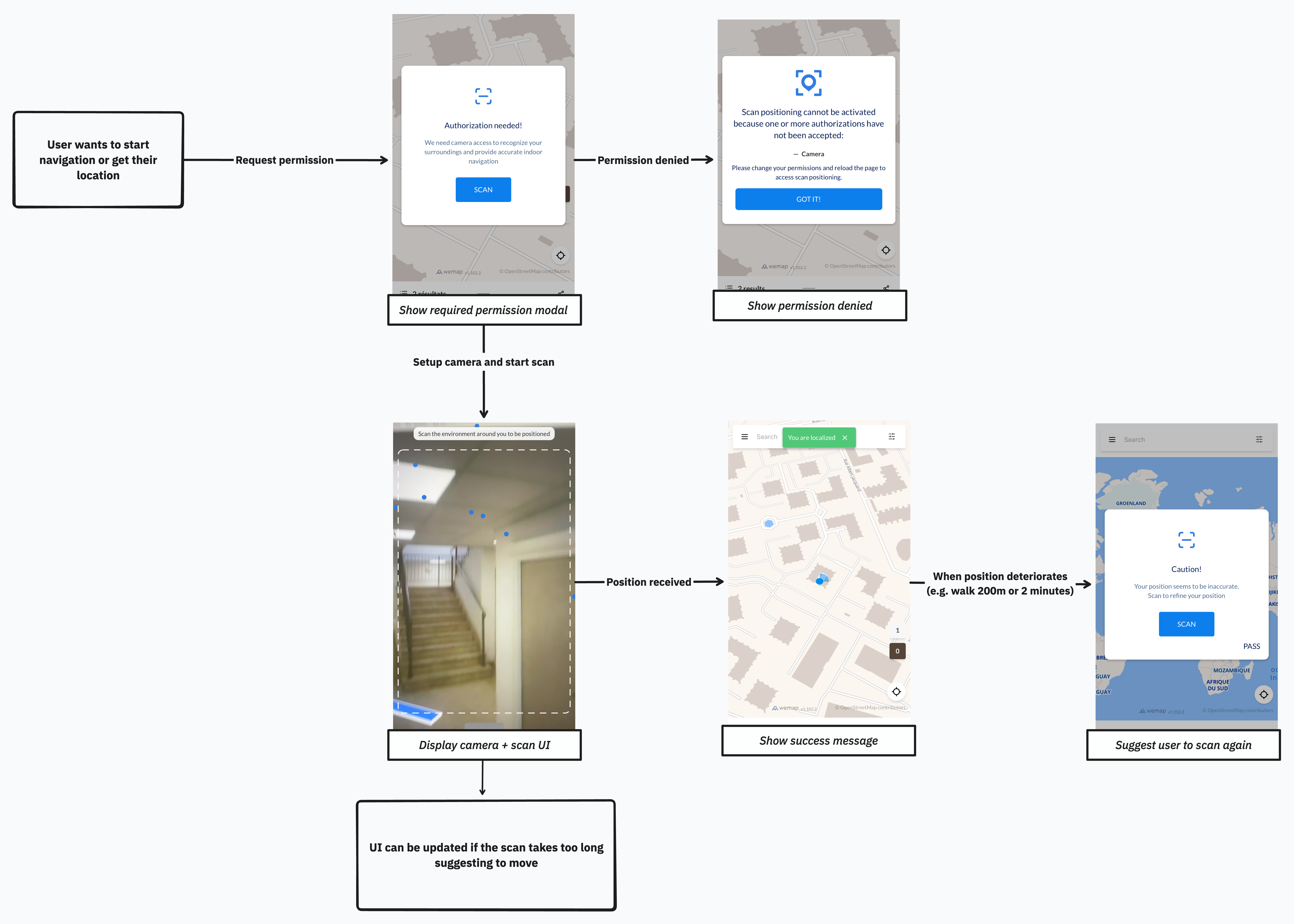
 Example of the authorization flow
Example of the authorization flow
Permission Denial Handling
If users deny permissions, provide:
- Clear explanation of what features won't work
- Easy path to re-enable permissions in settings
Visual indicators:
- Use distinct visual states for granted/denied permissions
- Show permission status in your UI
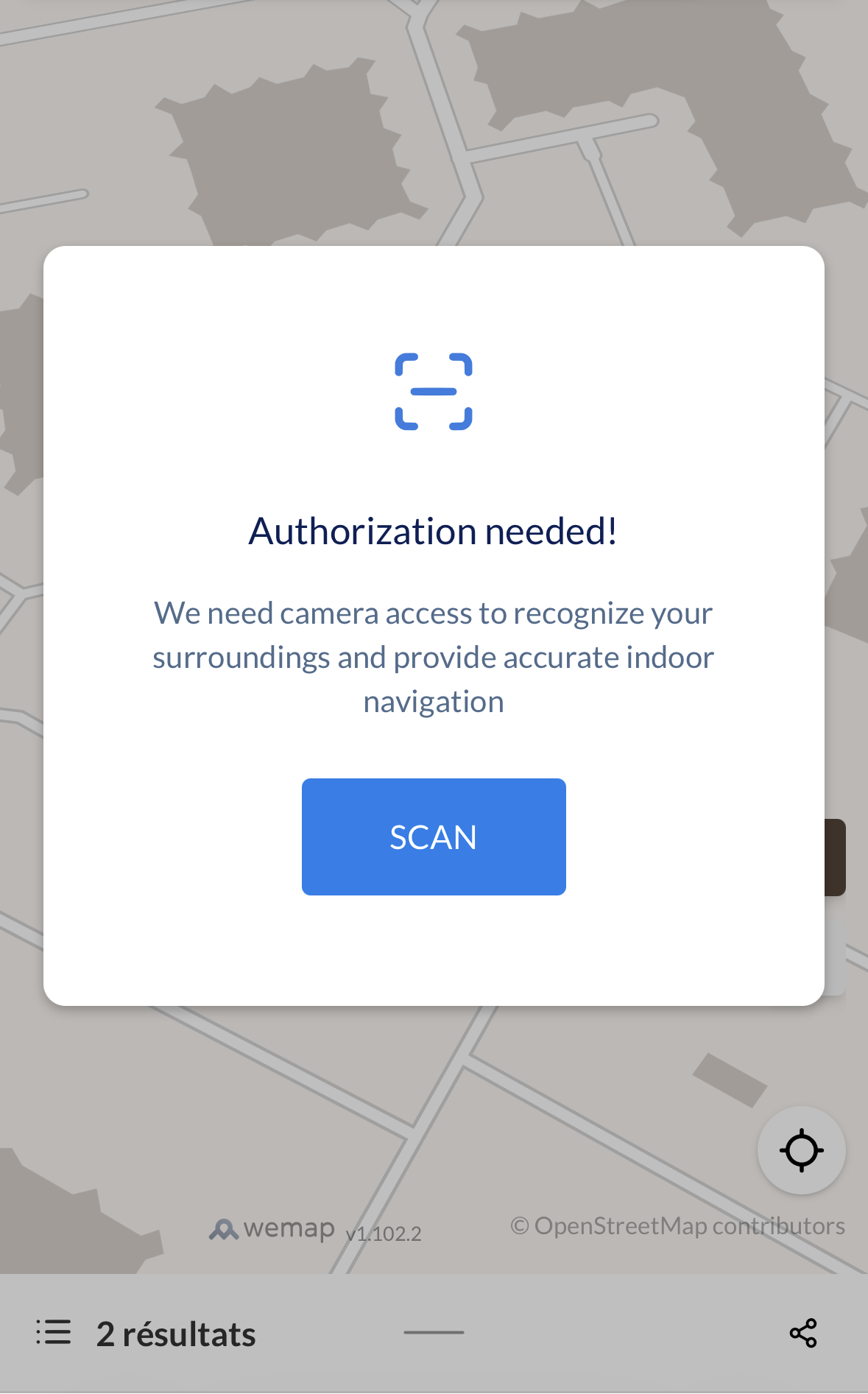
 Example of the camera unavailable state
Example of the camera unavailable state
Scanning Experience
Visual Feedback During Scan
During the scanning process, users need clear feedback about what's happening:
Loading states:
- Show a clear "Scanning..." indicator
- Use animations to indicate active processing
User guidance:
- Display instructions on screen: "Point camera at your surroundings"
- Show movement guidance: "Move slowly and steadily"
- Provide visual frame guides or targeting indicators to help users aim the camera
Scan duration:
- Set expectations: "This will take a few seconds"
- Provide feedback when scan completes successfully
Example of the scanning interface
Layout Recommendations
Camera container placement:
- Consider fullscreen mode for initial scan to maximize camera view
Error Handling & User Communication
Common Failure Scenarios
Scan loading timeout:
If a scan fails and no position is found, the system will not return error but will try to send another scan request, it will continue to do so until a position is found or the user cancels the scan.
The VPS system needs well textured surfaces to work properly. So if the scan takes longer than expected (approx. 5 seconds), you can suggest the user to point the camera at a different location.
Scan Triggers & Timing
When to Trigger Scans
Initial scan:
- Trigger when user wants to start a navigation or get his location
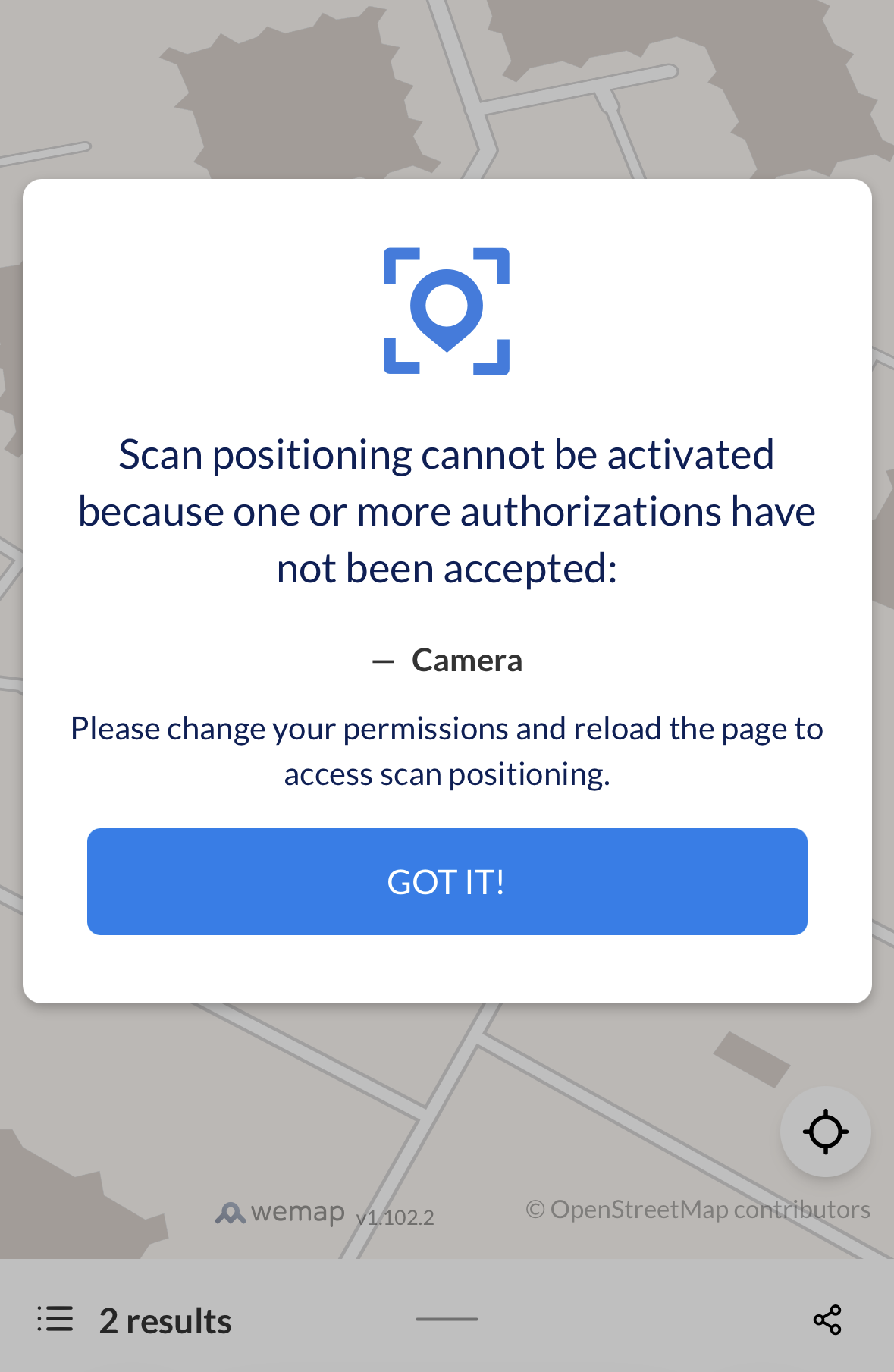
Manual re-scan:
- Suggest the user to scan again when the position is inaccurate (after approx. 200 meters of walk or 2 minutes of time)
When scan succeeds:
- Show clear success indicator (checkmark, success message)
- Confirm position found
Camera Resource Management
When to release camera:
- After successful scan
- When the user cancels the scan
User Flow